Machine Learning in Information Systems Research
文章链接:https://misq.umn.edu/misq/downloads/download/editorial/752/
作者:Padmanabhan, B., Fang, X., Sahoo, N., & Burton-Jones, A.
时间:Mar 2022
期刊:MISQ
总结:对IS研究中ML进行了总结分类,但视角偏design science
个人观点:强调了design science需要理论支撑,值得学习
摘要
Having given this context, we are now excited to get into the first genre of the series: machine learning (ML) research. ML plays an increasingly important role in IS research. We can broadly distinguish between two types of ML research in our field (which can also be combined).
One type seeks to study ML-related phenomena in a particular context, such as how ML is developed, used, and to what effect in a particular organization or industry. Such research can use a range of methods, such as surveys, simulations, and ethnography, among others. Our special issue on Managing AI exemplifies this approach (Berente et al. 2021).
The second type of ML research in IS seeks to apply and/or extend ML itself to make contributions, whether by contributing new ML methods, improving our understanding of IS phenomena through analyses enabled by ML, or advancing our knowledge of complex systems through understanding the role of ML in those systems. It is this second category that we will be covering in this editorial.
ML in IS Research: Types of Contributions
Type I: ML Methods Development
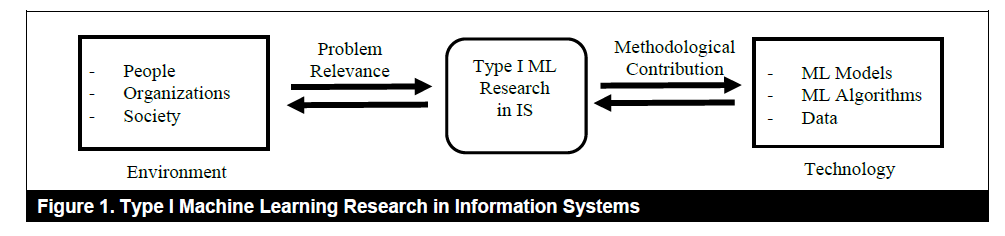
该类研究属于design science,旨在通过开发模型和算法解决商业中的问题。在进行该类研究时需要考虑两个贡献:
- Methodological novelty:如上图的右半部分所示,研究需要对已有的技术库进行充分检索,通过与基准方法进行对比或消融实验,证明研究的方法论贡献。(这部分和ML研究思路一致)
- Conceptual novelty:如上图的左半部分所示,研究需要基于理论和商业实践,总结目前存在的问题,并基于理论和商业实践指导算法的设计。(这部分体现了IS中design science的独特之处,需要紧密地和商业实践结合,并受到现有理论的指导。有代表性的文章是Fang and Hu, 2018)
Type II: Understanding Phenomena using ML
该类研究旨在通过机器学习算法对数据进行挖掘分析,增加对商业现象的理解。可以进一步分为3类:
- ML for Causal Inference:利用机器学习算法对非结构数据进行分析,提取新的解释变量;利用随机森林等算法分析因果关系;
- Domain-Specific Custom Statistical Model:构建、估计统计模型,以理解新现象。(这部分最好去读论文来理解)
- Structural Econometric Models:构建结构模型理解新现象。(同上,去读参考文献)
Type III: ML in Complex Systems
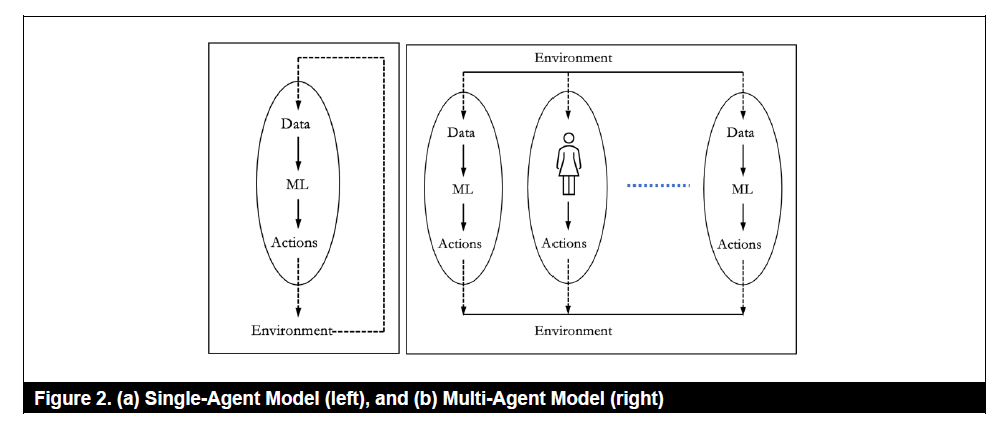
从复杂系统的角度考虑ML对商业环境的改变,如:
-
机器学习(如推荐系统)对环境(用户行为)进行改变,反过来通过数据影响机器学习本身
-
机器学习(如双边市场中针对买方的算法)同时影响其他机器学习算法(针对卖方的算法)、人类的行为以及自己本身